The paper of NIOCh's researcher Grigoriev I.A. (co-author) is published in the journal е The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, Vol. 158, 1 April 2020, 104748, (IF 3,481)
Paramagnetic bioactives encapsulated in poly(D,L-lactide) microparticules: Spatial distribution and in vitro release kinetics
Golubeva E.N., Chumakova N.A., Kuzin S.V., Grigoriev I.A., Kalai T., Korotkevich A.A., Bogorodsky S.E., Krotova L.I., Popov V.K., Lunin V.V.First published: 11 December 2019
doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2019.104748
Abstract
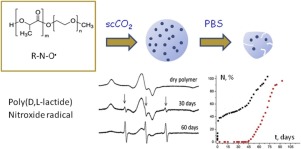
Poly(D,L-lactide) microparticles impregnated with a number of bioactive paramagnetic compounds have been fabricated using two SCF techniques: 1). PGSS (Particles from Gas Saturated Solution) and 2). polymer plasticization and swelling by supercritical carbon dioxide followed by its cryomilling. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy manifested homogeneous spatial distribution for the most of these substances encapsulated into the polymer. Irreversible relaxation processes in the prepared polymer structures and formulations were not observed. The qualitative difference in the release kinetics of paramagnetic molecules of different structure from the polymer microparticles into the phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH = 7.4) was demonstrated. pH-sensitive ATI spin probe proved the decrease (up to ≤ 4.5) of local pH inside the microparticles during the first 9 days after its immersion in PBS.
Altmetrics: