The paper with the participatin of NIOCh's researchers Olga Yu.Rogozhnikova, Dmitry V.Trukhin, Victor M.Tormyshev (international collaboration) is published in the Journal Free Radical Biology and Medicine (IF=6,02)
A radical containing injectable in-situ-oleogel and emulgel for prolonged in-vivo oxygen measurements with CW EPR
Lisa Lampp, Olga Yu.Rogozhnikova, Dmitry V.Trukhin, Victor M.Tormyshev, Michael K.Bowman, Nllathamby Devasahayam, Murali C.Krishna, Karsten Mäder, Peter ImmingFree Radical Biology and Medicine,
Volume 130, January 2019,, Pages 120-127
First published: 05 October 2018
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.10.442
Abstract
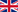
Molecular oxygen, reactive oxygen species and free radicals derived from oxygen play important roles in a broad spectrum of physiological and pathological processes. The quantitative measurement of molecular oxygen in tissues by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) has great potential for understanding and diagnosing a number of diseases, and for developing and guiding therapies. This requires improvements in the free radical probe systems that sense and report molecular oxygen levels in vivo. We report on the encapsulation of existing free radical probes in lipophilic gel implants: an in-situ-oleogel and an emulgel, based only on well-known, safe excipients for the incorporation of lipophilic and hydrophilic radicals, respectively. The EPR signals of encapsulated radicals were not altered compared to dissolved radicals. The high solubility of oxygen in lipophilic solvents enhanced oxygen sensitivity. The gels extended the lifetime of the radicals in tissues from tens of minutes to many days, simplifying studies with extended series of measurements. The encapsulated radicals showed a good in vivo response to changes in oxygen supply and seem to circumvent concerns from toxicity of the radical probes. These gels simplify the development of new oxygen-sensitive free radical probes for EPR oximetry by making their in vivo stability, persistence and toxicity a function of the encapsulating gel and not a set of additional requirements for the free radical probe.
Altmetrics:
Метрики PlumX теперь доступны в Scopus: узнайте, как другие ученые используют ваши исследования