The article with participation of NIOCh's researcher is published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, (IF 6,475)
An Updated View of Primary Ionization Processes in Polar Liquids
Irina V. Beregovaya, Irina S. Tretyakova, and Vsevolod I. BorovkovThe Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2021, 12, 47, 11573-11577
Publication Date (Web):November 22, 2021
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c03388
Abstract
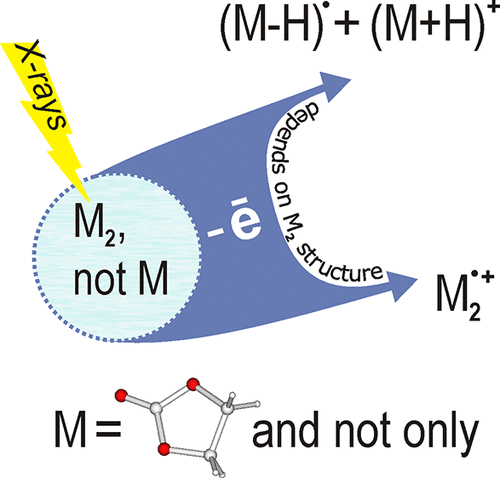
According to picosecond radiolysis data, primary radical cations in irradiated carbonates are very rapidly deprotonated. At the same time, analysis of the radiation-induced fluorescence from carbonate solutions indicates the formation of solvent-related radical cationic species with a relatively long lifetime. We use quantum chemical methods to develop a model of carbonate ionization that reconciles these conflicting data. Using ethylene carbonate as an example and assuming that its molecules exist in solution as a collection of dimeric associates, we show that both processes are the result of the loss of an electron from such dimers. This demonstrates that the generally accepted conceptualization of a primary ionization event, based on the idea of the formation of a radical cation of an individual molecule of an irradiated substance, requires revision in the case of polar aprotic liquids that tend to form molecular associates.
Альметрики: