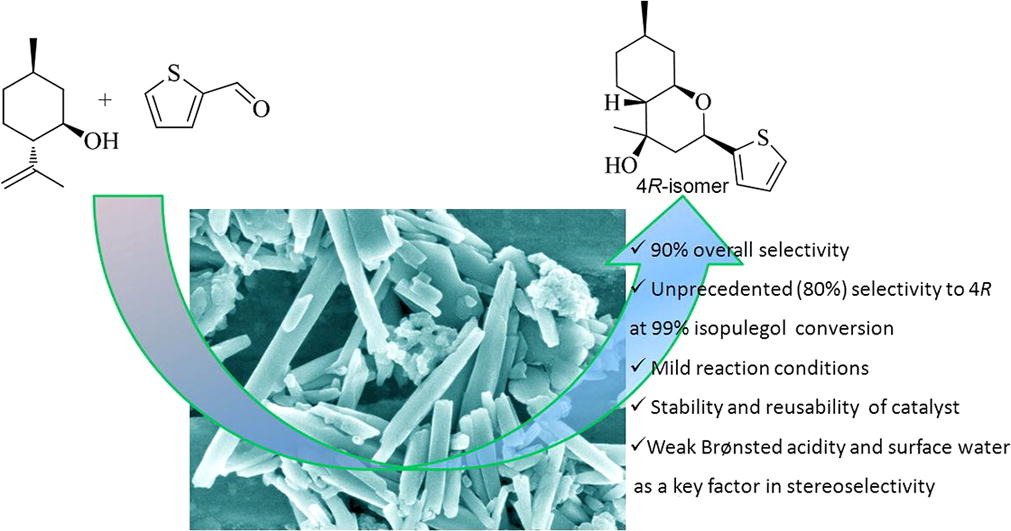
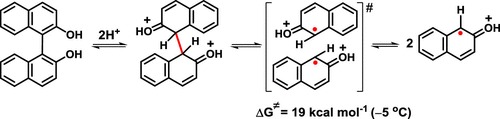
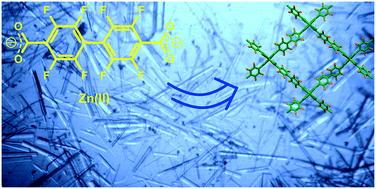
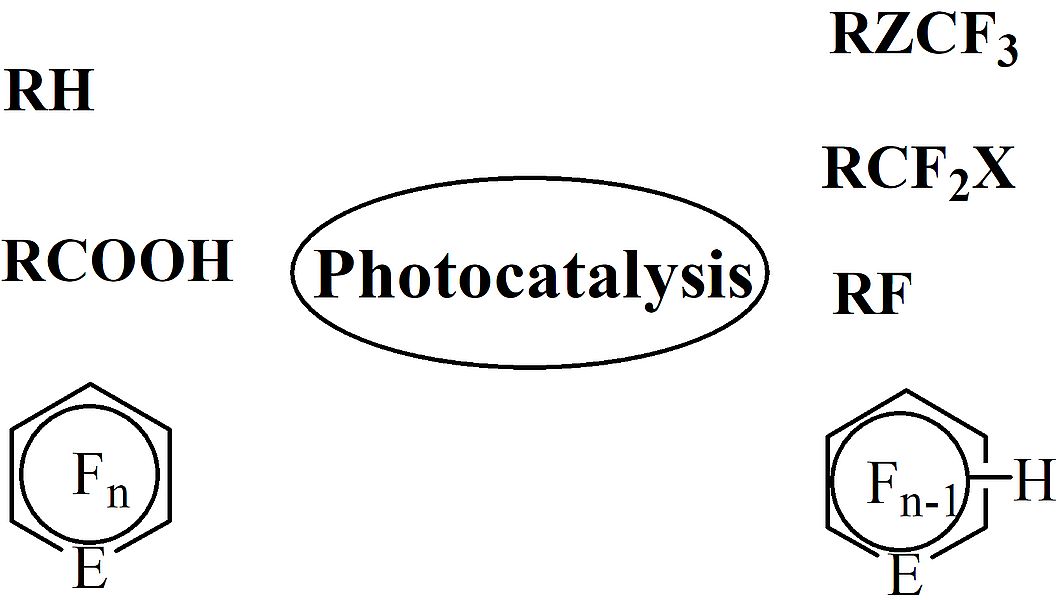
На сайте журнала Applied Sciences, (IF 2,217I) опубликована статья с участием сотрудников Института - Е.С. Можайцева, А..А. Мункуева, Е.В. Суслова , Д.В. Корчагиной, К.П. Волчо и Н.Ф. Салахутдинова
Редакция журнала обозначила статью "Избранное"
Featur Paper
The Development of Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase 1 Inhibitors. Combination of Monoterpene and Adamantine Moieties via Amide or Thioamide Bridges
Arina A. Chepanova, Evgenii S. Mozhaitsev, Aldar A. Munkuev, Evgeniy V. Suslov, Dina V. Korchagina, Olga D. Zakharova, Alexandra L. Zakharenko, Jinal Patel, Daniel M. Ayine-Tora, Jóhannes Reynisson, Ivanhoe K. H. Leung, Konstantin P. Volcho, Nariman F. Salakhutdinov and Olga I. LavrikAppl. Sci. 2019, 9(13), 2767;
DOI: https://10.3390/app9132767
Abstract
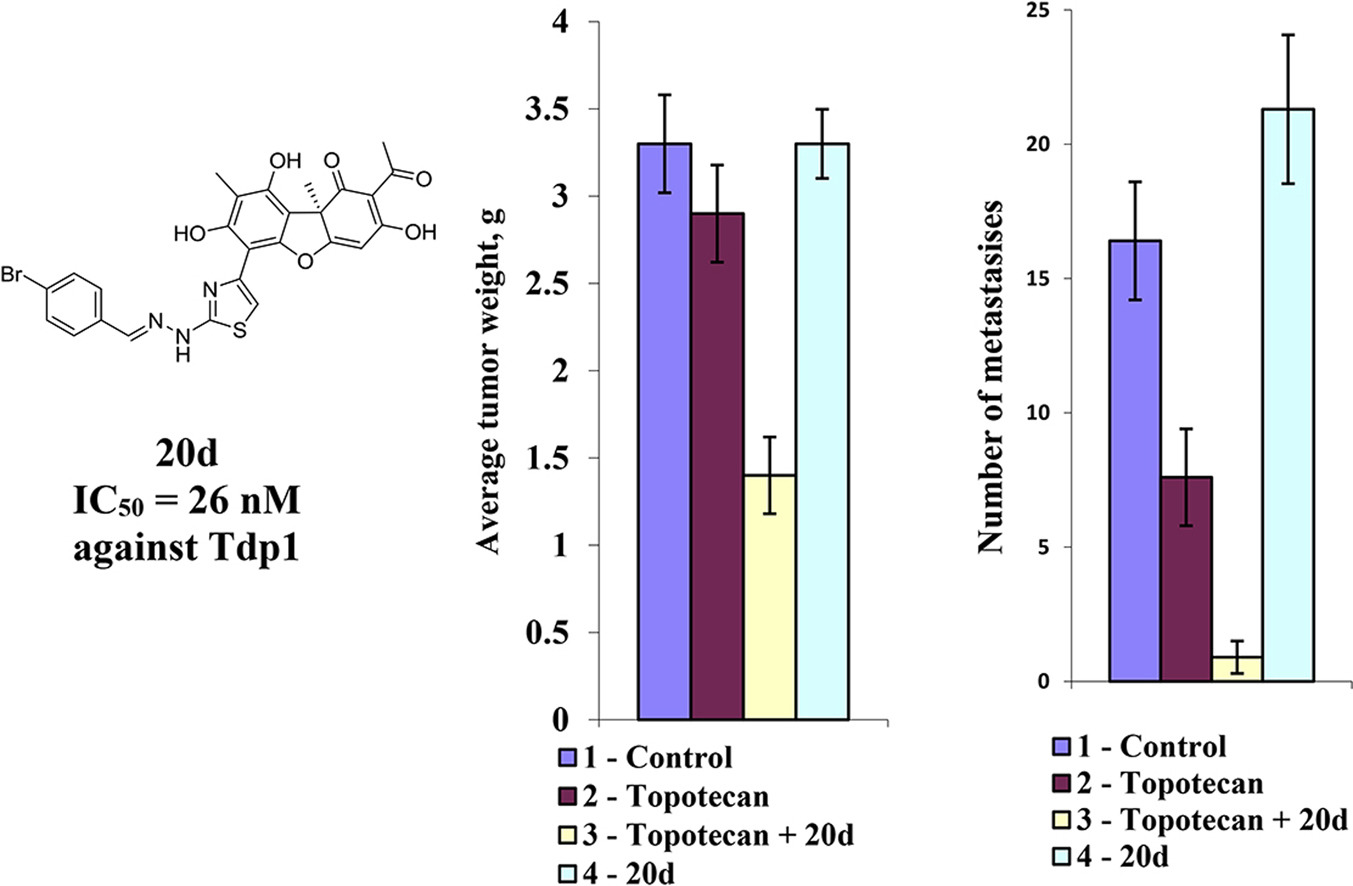
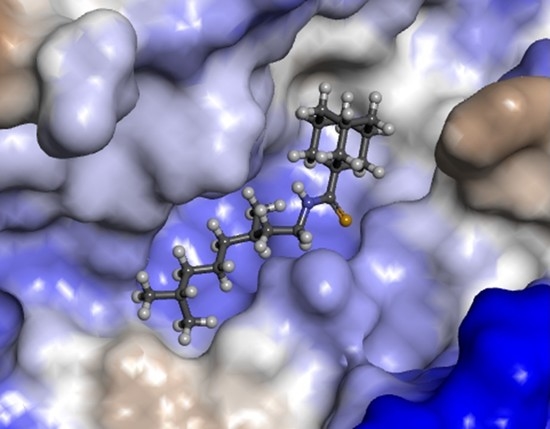
Eleven amide and thioamide derivatives with monoterpene and adamantine substituents were synthesised. They were tested for their activity against the tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 DNA (Tdp1) repair enzyme with the most potent compound , having an IC50 value of 0.64 µM. When tested in the A-549 lung adenocarcinoma cell line, no or very limited cytotoxic effect was observed for the ligands. However, in conjunction with topotecan, a well-established Topoisomerase 1 (Top1) poison in clinical use against cancer, derivative 46a was very cytotoxic at 5 µM concentration, displaying strong synergism. This effect was only seen for 46a (IC50—3.3 µM) albeit some other ligands had better IC50 values. Molecular modelling into the catalytic site of Tdp1 predicted plausible binding mode of 46a, effectively blocking access to the catalytic site. Full article
Альметрики: