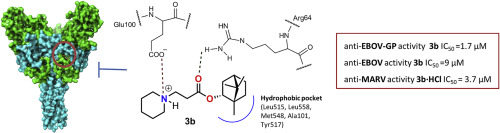
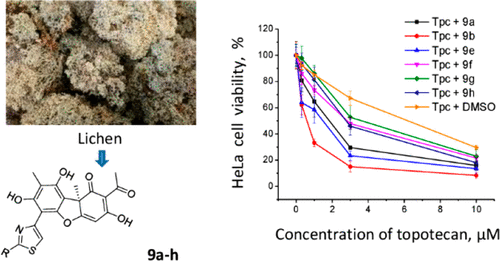
На сайте журнала Bioorganic Chemistry (IF 4,567) опубликована статья с участием сотрудников Института к.т.н. С.А. Попова (снс, ЛМХ ) и д.х.н., проф. Э.Э. Шульц (завлаб ЛМХ):
Design and Linkage Optimization of Ursane-Thalidomide-Based PROTACs and Identification of Their Targeted-Degradation Properties to MDM2 Protein
Abstract
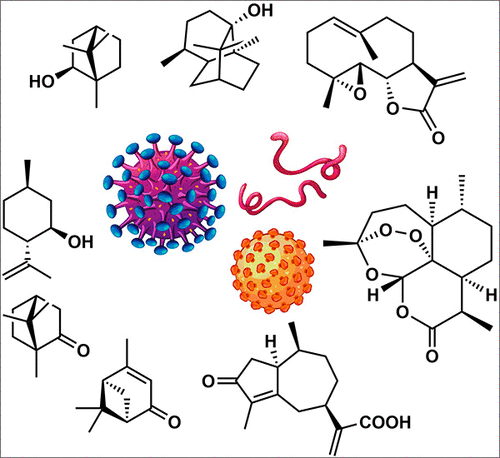
Ursolic acid (UA) is an accessible triterpenoid, widely applied in the design and synthesis of antitumor compounds. However, the mechanism of its anti-tumor effect is still unclear. To verify the molecular mechanism of its biological activity, based on the bifunctional activity of ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of the target protein of the proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) strategy, here we report the design, synthesis and cellular activity of six UA PROTAC hydrochloride compounds 1A-1F, in which UA acts as the binding ligand of the PROTAC and is linked to thalidomide (E3 ligand) through a series of synthetic linkers. The results revealed that compound 1B, connected with a POE-3 (3-Polyoxyether) possessed remarkable in vitro antitumor activity (with the IC50 value of 0.23∼0.39 μM against A549, Huh7, HepG2). WB results demonstrated that the administration of compound 1B induced significant degradation of MDM2 (only 25% to that of SM1), and promoted the expression of P21 and PUMA proteins, and thus inhibited the proliferation (77.67% of 1B vs 60.37% of CON in G1 phase) and promoted the apoptosis (26.74% of 1B vs 3.35% of CON) of A549 cells. This work demonstrated proof of designing the efficient target protein degradation by UA PROTACs with the POE linkers. In addition, we confirmed that UA possess the characteristic of targeted-binding the protein of murine double minute-2 protein (MDM2). This will lay a foundation for the comprehensive utilization of forest natural compound UA.
Альметрики:






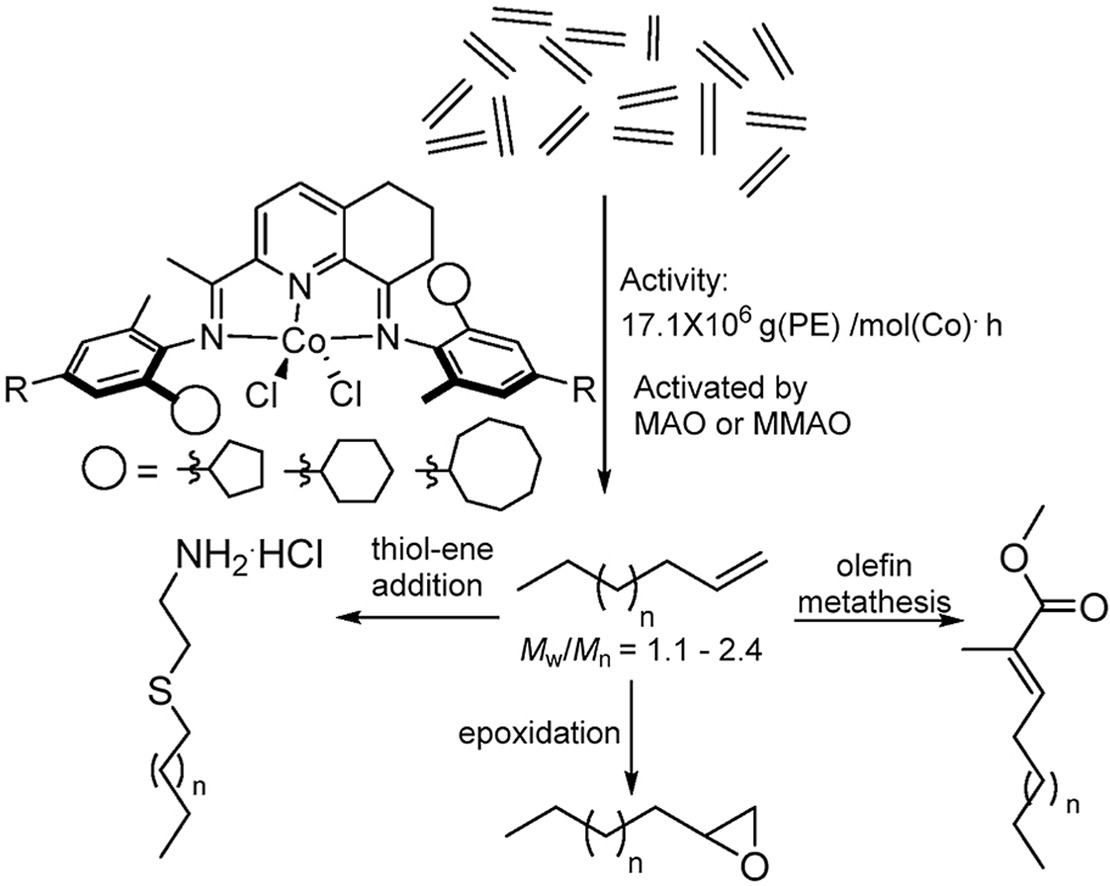
 CCH3)-8-(ArN)-5,6,7-C9H8N]CoCl2 (Ar = 2-(C5H9)-6-MeC6H3 Co1, 2-(C6H11)-6-MeC6H3 Co2, 2-(C8H15)-6-MeC6H3 Co3, 2-(C5H9)-4,6-Me2C6H2 Co4, 2-(C6H11)-4,6-Me2C6H2 Co5, 2-(C8H15)-4,6-Me2C6H2 Co6), distinguishable by the ring size of the ortho-cycloalkyl substituent and type of para-R group, have been synthesized and characterized. A distorted square pyramidal geometry is a feature of the molecular structure of Co4 with the two ortho-cyclopentyl groups located on neighboring N-aryl groups trans-configured. Compounds Co1 – Co6, on activation with methylaluminoxane (MAO) or modified MAO (MMAO), proved highly productive catalysts for ethylene polymerization at 60 °C [up to 17.1 × 106 g (PE) mol−1(Co) h−1 for cyclopentyl-containing Co4/MAO]; even at 90 °C significant activity was attainable (up to 6.75 × 106 g (PE) mol−1(Co) h−1). Strictly linear polyethylene waxes of low molecular weight (ca. 1.50 kg mol−1), narrow dispersity (Mw/Mn range: 1.1–2.4) and incorporating high levels of vinyl end-groups were generated. Post-functionalization of these PE waxes by epoxidation, thiol-ene addition and cross-olefin metathesis to form e-PE, PE-S-CH2CH2NH2·HCl and PE-MMA, respectively, has been demonstrated. For comparative purposes, [2-(ArN
CCH3)-8-(ArN)-5,6,7-C9H8N]CoCl2 (Ar = 2-(C5H9)-6-MeC6H3 Co1, 2-(C6H11)-6-MeC6H3 Co2, 2-(C8H15)-6-MeC6H3 Co3, 2-(C5H9)-4,6-Me2C6H2 Co4, 2-(C6H11)-4,6-Me2C6H2 Co5, 2-(C8H15)-4,6-Me2C6H2 Co6), distinguishable by the ring size of the ortho-cycloalkyl substituent and type of para-R group, have been synthesized and characterized. A distorted square pyramidal geometry is a feature of the molecular structure of Co4 with the two ortho-cyclopentyl groups located on neighboring N-aryl groups trans-configured. Compounds Co1 – Co6, on activation with methylaluminoxane (MAO) or modified MAO (MMAO), proved highly productive catalysts for ethylene polymerization at 60 °C [up to 17.1 × 106 g (PE) mol−1(Co) h−1 for cyclopentyl-containing Co4/MAO]; even at 90 °C significant activity was attainable (up to 6.75 × 106 g (PE) mol−1(Co) h−1). Strictly linear polyethylene waxes of low molecular weight (ca. 1.50 kg mol−1), narrow dispersity (Mw/Mn range: 1.1–2.4) and incorporating high levels of vinyl end-groups were generated. Post-functionalization of these PE waxes by epoxidation, thiol-ene addition and cross-olefin metathesis to form e-PE, PE-S-CH2CH2NH2·HCl and PE-MMA, respectively, has been demonstrated. For comparative purposes, [2-(ArN


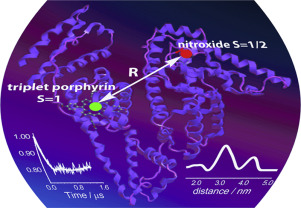
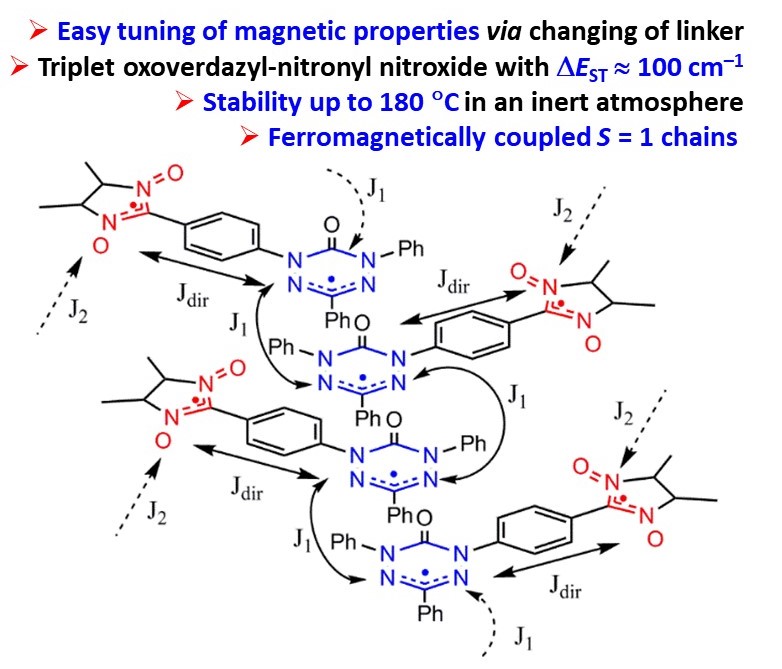
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N(O)–tert-Bu coupler) was investigated under various conditions. It was found that prolongation of reaction time caused transformation of the initial diradical into new diradicals with the unique >C
N(O)–tert-Bu coupler) was investigated under various conditions. It was found that prolongation of reaction time caused transformation of the initial diradical into new diradicals with the unique >C